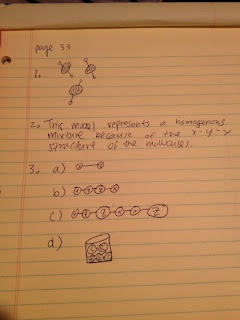Thursday, June 27, 2013
Blog Question
The solve a solution concentration problem, you divide the mass of the solute by the mass of the solution. Next you multiply it by 100. Calculating the percent of the mass is a the trickiest part.
Homework # 9
1)
a. Since you would cool the solution,
it would become a supersaturated.
b.
2)
ii.
25 grams of water must evaporate because some of the water has already done so
3)
c.
Because the drawing of figure B has a higher water level, water is more
diluted. Therefore, the KCl is more spread out. Both drawings show saturated
mixtures, yet figure B is much more saturated.
Wednesday, June 26, 2013
Blog Question
Having the chart from page 54 in front of me helped my solve the solubility homework questions. In addition, working with my classmates and discussing the different vocab terms helped me get a better understanding of the concepts in the chapter so the questions were easier for me to complete.
Homework # 8
C.2 page 56
6. a) 30 grams
b) supersaturated
c) 35 grams
7. a) The crystal will dissolve into the unsaturated solution
b) The crystals will remain undissolved at the bottom of the saturated solution
c) Solid crystals will form and will settle to the bottom of the supersaturated solution
8. 52.5% (1.5 x 35g = 52.5%)
1. A) 100 g
B) 45 g
2. A) 10 g
B) 20 g
3. A) 87.5 g KNO3
B) at least 80 g
B) 45 g
2. A) 10 g
B) 20 g
3. A) 87.5 g KNO3
B) at least 80 g
ISCS #1-8 (page 52)
1. Because higher tempatures dissolve the slutes more easily.
2. 50 grams (from the chart on page 54)
3.
a) 200 grams
b) 710 grams
c) 1,892 grams
4.
a) 20- KNO3, NaCl, KCl
b) 80- KNO3, KCl, NaCl
5. Saturated- when there is too much chemical for the water. Unsaturated- contains less disolved substance than it can hold
6. a) 30 grams
b) supersaturated
c) 35 grams
7. a) The crystal will dissolve into the unsaturated solution
b) The crystals will remain undissolved at the bottom of the saturated solution
c) Solid crystals will form and will settle to the bottom of the supersaturated solution
8. 52.5% (1.5 x 35g = 52.5%)
Blog Question
I learned from the water testing lab that certain ions are not visible. Therefore, it is hard to judge which samples from the well plate fully reacted when chemicals were added to them. I think that learning how to safely conduct lab procedures is a very fun and educational experience.
Tuesday, June 25, 2013
Homework # 7
1SBS #25-34
25. Qualitative tests identify the presence or absence of a specific substance in a sample. Quantitate tests determine the quantity of a specific substance present in a sample.
26. A confirming test positivley confirms that a certain ion is present.
27.
a) I used a reference solution because a reference solution is used for comparison.
b)I used distilled water in the blank because it is unknown if it contains ions
28. Yes; iron is present because the test was positive.
29. Personally, I would test out the Tyndall effect and try to pass light through the water.
30. Since medicine is typically a colloid, it needs to be shaken before you drink it so you can put all the proper elements in the medicine into your body instead of just the top layer of the medicine.
31. It is useful for element symbols to have international acceptance so that the periodic table can be read by everyone.
32.
33. It is impossible for water to be completley free of chemicals because some gasses will always dissolve in water to some extent.
34. H20 is a liquid made of Oxygen and Hydrogen gasses and when put together they make a liquid (at room temperature).
25. Qualitative tests identify the presence or absence of a specific substance in a sample. Quantitate tests determine the quantity of a specific substance present in a sample.
26. A confirming test positivley confirms that a certain ion is present.
27.
a) I used a reference solution because a reference solution is used for comparison.
b)I used distilled water in the blank because it is unknown if it contains ions
28. Yes; iron is present because the test was positive.
29. Personally, I would test out the Tyndall effect and try to pass light through the water.
30. Since medicine is typically a colloid, it needs to be shaken before you drink it so you can put all the proper elements in the medicine into your body instead of just the top layer of the medicine.
31. It is useful for element symbols to have international acceptance so that the periodic table can be read by everyone.
32.
33. It is impossible for water to be completley free of chemicals because some gasses will always dissolve in water to some extent.
34. H20 is a liquid made of Oxygen and Hydrogen gasses and when put together they make a liquid (at room temperature).
Monday, June 24, 2013
Blog Question
How does testing water help us?
Testing water helps students to understand the process of working in a lab which expands our skill and knowladge of science.
Homework # 6
ISBS #19-24 p. 51
19.
a. Carbon: 6 protons, 6 electrons
b. Aluminum: 13 protons, 13 electrons
c. Lead: 82 protons, 82 electrons
d. Chlorine: 17 protons, 17 electrons
20.
a. Sulfur: no
b. Iron: no
c. Silver: yesd
d. Iodine: no
21.
a. an ion
b. electrically neutral
c. electrically neutral
d. cation
e. cation
22.
a. losing electrons
23.
a. H
24.
19.
a. Carbon: 6 protons, 6 electrons
b. Aluminum: 13 protons, 13 electrons
c. Lead: 82 protons, 82 electrons
d. Chlorine: 17 protons, 17 electrons
20.
a. Sulfur: no
b. Iron: no
c. Silver: yesd
d. Iodine: no
21.
a. an ion
b. electrically neutral
c. electrically neutral
d. cation
e. cation
22.
a. losing electrons
b. neither
c. neither
d. gaining electrons
e. gaining electrons
23.
a. H
b. Na+
c. Cl-
d. Al+
24.
a. KI -potassium iodine
b. CaS -calcium sulfur
c. FeBr - iron bromine
d. BaOH - barium oxygen hydrogen
e. NHPO - nitrogen hydrogen phosphorous oxygen
f. AlO - aluminum oxygen
Water Diary
|
Categories
|
Day 1
|
Day 2
|
Day 3
|
||
|
# of people
|
2
|
4
|
4
|
||
|
# of baths (average- 15 min)
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
||
|
# of showers (average- 10-15 min)
|
1
|
4
|
3
|
||
# of toilet flushes
|
5
|
9
|
10
|
||
|
# of hand washed loads of dishes
|
1
|
2
|
2
|
||
|
# of machine washed loads of dishes
|
1
|
2
|
2
|
||
|
# of lawn waterings (sprinklers- 20
min average)
|
2
|
2
|
2
|
||
|
Number of cups of water used for
cooking and drinking
|
5
|
11
|
10
|
||
|
Number of times water runs in the
sink
(average- 1 min 30 sec)
|
7
|
10
|
9
|
||
|
Number of times washing hands
|
6
|
11
|
10
|
||
Sammy
Weiser’s Water Diary
|
Laundry
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
Blog Question
My favorite thing we did the first week was purify the foul water. I liked seeing the process of making the water clear and odorless because I didn't think it was possible. I also liked learning how to work in a lab.
Homework # 5
A.7- Water use analysis (page 20-2)
1. 10, 717
2. 714.5
3.
4. The range of the average daily personal water use in my class is 1, 493.
5. The mean for my class data is 600 L and the median is 579 L.
6. We water our yards year-round, plus we live in a desert so our class's families use more water.
7. The household is closer
What do our overall results tell us? Aggregated?
Our overall class results tell us that our families typically have large lawns or many plants that require a large amount of water to keep them alive. Thus, our families use alot of water so we can water all our plants.
ISBS page 52
13.
14. a) i, ii, vi
b) iii, iv, v
15. atomic weight & atomic number of an element
16. a) 3 Hydrogen atoms, 1 Phosphorus atom , and 4 Oxygen atoms
b) 1 Sodium atom, 1 Oxygen atom, and 1 Hydrogen atom
c) 1 Sulfur atom, and 2 Oxygen atoms
1. 10, 717
2. 714.5
3.
4. The range of the average daily personal water use in my class is 1, 493.
5. The mean for my class data is 600 L and the median is 579 L.
6. We water our yards year-round, plus we live in a desert so our class's families use more water.
7. The household is closer
What do our overall results tell us? Aggregated?
Our overall class results tell us that our families typically have large lawns or many plants that require a large amount of water to keep them alive. Thus, our families use alot of water so we can water all our plants.
ISBS page 52
13.
14. a) i, ii, vi
b) iii, iv, v
15. atomic weight & atomic number of an element
16. a) 3 Hydrogen atoms, 1 Phosphorus atom , and 4 Oxygen atoms
b) 1 Sodium atom, 1 Oxygen atom, and 1 Hydrogen atom
c) 1 Sulfur atom, and 2 Oxygen atoms
c) a. 2 hydrogen + 2 chlorine --> 2 hydrogen and chlorine. b. 2 compounds of hydrogen and oxygen --> 2 water + 2 oxygen.
18. a) Na9 HCO3 + HCl --> NaCl + H2O + CO2
b) C6 H12 O6 + O6 --> CO6 3 H2O
Friday, June 21, 2013
Extra Credit
"Grassed Up"
Africa's famous grasslands have recently been said to have a great connection to human evolution. Many people think that we walk upright because our ancestors had to walk upright in order to see over the tall grass. Certain people argue that when the savannas came into existence, evolution intensely sped up and caused our ancestors to adapt or die out. A paper in Geology, written by Sarah Feakins at the University of Southern California suggests that our ancestors walking upright to see over the tall grass did not have anything to do with the savannahs. Feakins discovered 12 million year old plant molecules that contained carbon and carbon atoms which come in many different isotopes (variants of a particular chemical element), making it easy to decode their history. Feakins discovered that the grass changed as species adapted to drier weather. The climatic change was the reason people suspected to savnnah of excellerating human evolition. Although, Feakins proves that east Africa was never heavy with tall grass, therefore. it is impossible that our ancestors starting walking upright due to their need to see over the grass. This ecological explination that was created is certainly wrong.
(http://humanorigins.si.edu/research/climate-research/effects)
(http://www.livescience.com/15377-savannas-human-ancestors-evolution.html)
Africa's famous grasslands have recently been said to have a great connection to human evolution. Many people think that we walk upright because our ancestors had to walk upright in order to see over the tall grass. Certain people argue that when the savannas came into existence, evolution intensely sped up and caused our ancestors to adapt or die out. A paper in Geology, written by Sarah Feakins at the University of Southern California suggests that our ancestors walking upright to see over the tall grass did not have anything to do with the savannahs. Feakins discovered 12 million year old plant molecules that contained carbon and carbon atoms which come in many different isotopes (variants of a particular chemical element), making it easy to decode their history. Feakins discovered that the grass changed as species adapted to drier weather. The climatic change was the reason people suspected to savnnah of excellerating human evolition. Although, Feakins proves that east Africa was never heavy with tall grass, therefore. it is impossible that our ancestors starting walking upright due to their need to see over the grass. This ecological explination that was created is certainly wrong.
(http://humanorigins.si.edu/research/climate-research/effects)
(http://www.livescience.com/15377-savannas-human-ancestors-evolution.html)
Thursday, June 20, 2013
Wednesday, June 19, 2013
Homework #3
ISAS page 50
1. A physical property is a physical charactieristic of a material that cn be directly measured or absorbed.
2. Ice, water from a lake, water vapor
3. They are equal in mass because no matter what their form is, they take up the same amount of space
4. In a factory where juice or drinks are produced
5. Heterogenous mixtures are mixtures that are not uniform throughout, while homogenous mixtures are uniform throughout.
6. You need to know if the gasoline and water will form a homogenous or heterogenous mixture to figure out which substance will float to the top.
7.
a) colloid
b) colloid
c) solution
d) solution
e) suspension
f) colloid
8. This demonstrates that the air in the room is a solution since the tydnall effect is taking place.
9.
10. This mixture is a solution since no particles are seperating. It is a homogenous solution to be more specific.
11. Substance: a material with a uniform and definate composition as well as distinct properties (example #1: water, example #2: oxygen)
12.
1. A physical property is a physical charactieristic of a material that cn be directly measured or absorbed.
2. Ice, water from a lake, water vapor
3. They are equal in mass because no matter what their form is, they take up the same amount of space
4. In a factory where juice or drinks are produced
5. Heterogenous mixtures are mixtures that are not uniform throughout, while homogenous mixtures are uniform throughout.
6. You need to know if the gasoline and water will form a homogenous or heterogenous mixture to figure out which substance will float to the top.
7.
a) colloid
b) colloid
c) solution
d) solution
e) suspension
f) colloid
8. This demonstrates that the air in the room is a solution since the tydnall effect is taking place.
9.
10. This mixture is a solution since no particles are seperating. It is a homogenous solution to be more specific.
11. Substance: a material with a uniform and definate composition as well as distinct properties (example #1: water, example #2: oxygen)
12.
a) compound
b) element
c) compound
d) element
e) compound
f) compound
g) element
Tuesday, June 18, 2013
Homework #2
ISAS page 23
3.
- Manufacture of the filter paper= indirect water use (running machinery, cleaning, and using water for the paper)
- Premoistening of the sand and gravel= direct water use. (measuring exactly how much water is used to moisten the gravel)
- Use of water to cool the distillation apparatus: direct water use. (measuring exact amount of water that is needed)
4. Puryfying water means
filtrating the water or cleansing the water of dirt or unwanted materials.
5. oil-water separation, sand
filtration, charcoal adsorption and filtration
6. During the oil-water
filtration, oil was removed from my sample of foul water. During the sand
filtration step, coffee grounds were removed from my sample. And during the
charcoal adsorption and filtration step, both the color and odor were removed
from the foul water sample.
7. The solid particles in the foul
water were heterogenous. But, on the contrary, salt water is homogenous. So,
since salt water is homogeneous foul water is heterogeneous, the same procedure
will not work for both types of water. To make the seawater drinkable, the water would need go through
distillation so the salt could be separated form the water.
pg. 22
- washing cars, showering, washing pots and pans
- drinking water to stay hydrated
- I could reduce my water use by taking shorter showers to conserve water.
- I could use impure water for washing my car. this water would be taken from dish washing.
Unit 1A Vocabulary List
Filtration: When solid particles are separated from a liquid by passing the mixture through a material that retains the solid particles and allows the liquid to pass through.
Filtrate: The liquid collected after it has been filtered.
Adsorbs: Attracts and holds on its surface.
Percent Recovery: The percent of original foul water recovered as purified water
Histogram: A graph compiling data from many groups
Range: The difference between the largest and smallest values in a set of data
Average: You get the average by adding the values together and dividing the sum by the total number of values
Mean: average
Median: The middle value
Electrical Conductivity: The presence of dissolved, electrically charged particles in water
Direct Water Use: Water use that can be directly measured
Indirect Water Use: secondary uses of water that are hidden and rarely noted
Aquifer: A water bearing layer of rock, sand, or gravel
Gaseous State: water vapor
Liquid State: regular water (lakes, rivers, ocean, etc.)
Solid State: everything has a solid state (example- ice is water in solid form)
Matter: Something that occupies space and has a mass
Physical Properties: Properties that can be measured and observed without changing its chemical makeup
Density: The mass of material within a given volume
Freezing Point: physical property & is at 0 Celsius
Aqueous Solution: Water solutions with liquids dissolved in them/ not fully pure water
Mixture: It is when 2 or more substances combine and retain their individual properties
Heterogeneous Mixture: A non universal mixture that isn't always the same
Suspension: A heterogeneous mixture with solid particles that are big enough to settle out or particles that can be separated by using filtration
Tyndall Effect: Where particles are too small to see, but large enough to reflect light coming from a beam to the left of the beakers
Colloid: A mixture with the Tyndall effect
Homogeneous Mixture: a universal mixture
Solutions: Homogeneous mixtures
Solute: A dissolved substance
Solvent: The dissolving agent
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)